Home › Forums › VACCINE INJURIES AND INFORMATION › Here is an organized library of more than one thousand peer reviewed articles which show that Covid-19 “vaccines” are harmful.
- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
2023-12-28 at 21:11 #433743
 Nat QuinnKeymaster
Nat QuinnKeymasterHere is an organized library of more than one thousand peer reviewed articles which show that Covid-19 “vaccines” are harmful.
Here is an ultimate and organized library to empower research, back up law suits, support criminal charges, or effect political change. It’s also abundant proof for anyone who is still buying the “safe and effective” claim, but is willing to look at the evidence. Please bookmark and share this page for ongoing reference.
Thanks to the community at CovidVaccineInjuries.com for their astronomical research compiling the basis of this visualized and indexed resource.
Our website and content output requires significant human resources to maintain, and we rely on community funding to remain operational. Please consider making a donation towards our cause. We appreciate all contributions.
Table of ContentsMyocarditis
Includes terms: Inflammatory Heart Reactions & Myocardial. Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium). The inflammation can reduce the heart’s ability to pump and cause rapid or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Signs and symptoms of myocarditis include chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and rapid or irregular heartbeats. In a small percentage of cases persons with myocarditis can be at risk of sudden death following strenuous activity. Some sufferers of myocarditis may require heart surgery or a heart transplant later in life.

Myocarditis Thrombosis
Includes terms: Thrombotic & Thromboembolic & Thromboembolism. There are three categories of causes of thrombosis: damage to the blood vessel (catheter or surgery), slowed bloodflow (immobility), and/or thrombophilia (if the blood itself is more likely to clot).

Deep Vein Thrombosis Thrombocytopenia
A condition in which there is a lower-than-normal number of platelets in the blood. It may result in easy bruising and excessive bleeding from wounds or bleeding in mucous membranes and other tissues.

Thrombocytopenia Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
A type of stroke in which the venous channels of the brain become thrombosed, resulting in cerebral infarction in the areas corresponding to the thrombosis.

MRI of Clot in Cerebral Venous Thrombosis | Stroke Vasculitis
Includes term: Microscopic polyangiitis. Inflammation of the blood vessels that causes changes in the blood vessel walls. When your blood vessel becomes weak, it might stretch and bulge (called an aneurysm). It might also burst open, causing bleeding. This can be life-threatening.

Vasculitis on inside of calves Guillain-Barré Syndrome
A neurological disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous system—the network of nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord. GBS can range from a very mild case with brief weakness to nearly devastating paralysis, leaving the person unable to breathe independently. Fortunately, most people eventually recover from even the most severe cases of GBS. After recovery, some people will continue to have some degree of weakness.

Guillain-Barre Sundrome Lymphadenopathy
Includes terms: Unilateral, Supraclavicular And Cervical. A disease affecting the lymph nodes where the sizes of the lymph can be affected.

Lymphadenopathy Anaphylaxis
Includes term: Anaphylactoid. A severe, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction.

Young woman experiencing anaphylactic shock Myopericarditis
A complication of acute pericarditis, is characterized by extension of pericardial inflammation to the myocardium, which manifests as an elevated troponin level. It is generally evaluated and treated as acute pericarditis.

Acute Pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium) Allergic Reactions
Includes Term: Allergy. A condition in which the immune system reacts abnormally to a foreign substance.

Allergic reaction (hives) on arm Bell’s Palsy
Includes Terms: Facial Paralysis & Facial Palsy. An unexplained episode of facial muscle weakness or paralysis. It begins suddenly and worsens over 48 hours. This condition results from damage to the facial nerve (the 7th cranial nerve). Pain and discomfort usually occur on one side of the face or head.

Bell’s Palsy on female face Axillary Adenopathy
Includes term: Adenopathy. Also called armpit lump, axillary lymphadenopathy occurs when your underarm (axilla) lymph nodes grow larger in size. While this condition may be concerning, it’s usually attributed to a benign cause. It may also be temporary.

Axillary adenopathy under right arm Pericarditis
Swelling and irritation of the thin, saclike tissue surrounding your heart (pericardium). Pericarditis often causes sharp chest pain and sometimes other symptoms. The chest pain occurs when the irritated layers of the pericardium rub against each other.

Comparison to normal heart Acute Myelitis
Includes Term: Transverse Myelitis. An inflammation of the spinal cord which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Inflammation in the spinal cord, can cause the myelin and axon to be damaged resulting in symptoms such as paralysis and sensory loss. Myelitis is classified to several categories depending on the area or the cause of the lesion; however, any inflammatory attack on the spinal cord is often referred to as transverse myelitis.

Acute Myelitis Perimyocarditis
An acute inflammation of the pericardium and the underlying myocardium resulting in myocellular damage. It is usually asymptomatic with complete resolution in most cases. It can however lead to fulminant cardiac failure resulting in death or requiring cardiac transplantation.

Intracerebral Haemorrhage
Includes Term: Stroke. Intracerebral hemorrhage (bleeding into the brain tissue) is the second most common cause of stroke (15-30% of strokes) and the most deadly. Blood vessels carry blood to and from the brain. Arteries or veins can rupture, either from abnormal pressure or abnormal development or trauma.
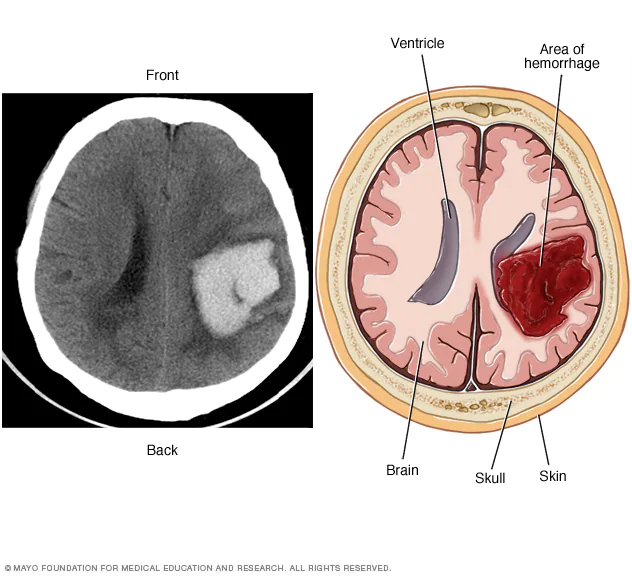
Intracerebral Haemorrhage Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
Defined as an elevation in the patient’s liver function tests that requires corticosteroids and that has no alternate etiology.

Immune-Mediated Hepatitis affects the liver Facial Nerve Palsy
Neurological Symptoms
Includes Terms: Neurological Side Effects & Neurological Complications. Medically defined as disorders that affect the brain as well as the nerves found throughout the human body and the spinal cord.
Human nervous system Haemorrhage
Includes terms: cerebral, lobar, acral and retinal. The release of blood from a broken bloody vessel, either inside or outside the body.

Retinal Haemorrhage Immune-Mediated Disease Outbreaks
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the body’s own cells. There are many types, including Coeliac disease, lupus and Graves’ disease. Although they can’t be cured, there are various treatment options to manage the symptoms and reduce further damage to your body.

Immune-Mediated Disease Outbreaks 19th to 21st century Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
A temporary heart condition that develops in response to an intense emotional or physical experience. It’s also known as stress cardiomyopathy or broken heart syndrome. In this condition, the heart’s main pumping chamber changes shape, affecting the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. Death is rare, but heart failure occurs in about 20% of patients. Rarely reported complications include arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), obstruction of blood flow from the left ventricle, and rupture of the ventricle wall.
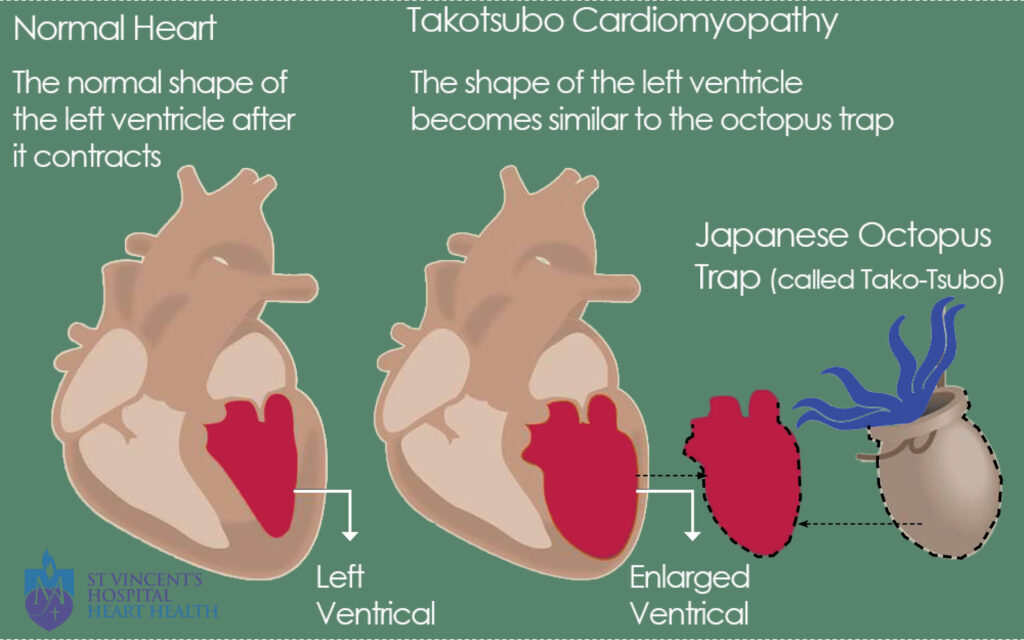
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy Cardiac
Cardiac complications include myocardial injury, heart failure (HF), cardiogenic shock, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults, and cardiac arrhythmias including sudden cardiac arrest.

Rhabdomyolysis
A serious syndrome due to a direct or indirect muscle injury. It results from the death of muscle fibers and release of their contents into the bloodstream. This can lead to serious complications such as renal (kidney) failure. This means the kidneys cannot remove waste and concentrated urine. In rare cases, rhabdomyolysis can even cause death.

Rhabdomyolysis – toxic muscular content leaks into bloodstream, resulting in coke-coloured urine Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
A disorder that causes blood clots (thrombi) to form in small blood vessels throughout the body. These clots can cause serious medical problems if they block vessels and restrict blood flow to organs such as the brain, kidneys, and heart.

Cardiovascular events
Acute Hyperactive Encephalopathy
Includes Terms: Acute Encephalopathy & Encephalitis. A general brain dysfunction due to significantly high blood pressure. Symptoms may include headache, vomiting, trouble with balance, and confusion. Onset is generally sudden. Complications can include seizures, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, and bleeding in the back of the eye.
Acute Kidney Injury
A sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that occurs within a few hours or a few days.

Multiple Sclerosis
A potentially disabling disease of the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).

Multiple Sclerosis: damage to the myelin exposes nerve fiber Henoch-Schonlein PurpuraAffects the small blood vessels of the skin, joints, intestines and kidneys. It’s most common before the age of seven but can affect anyone. A disorder causing inflammation and bleeding in the small blood vessels.

Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Bleeding Episodes
Major episodes include most joint bleeds, bleeding into large muscles, muscle bleeds with signs of compartment syndrome, life-threatening bleeds, and surgery. These usually require a 70% – 100% correction and more than one infusion. The exact dose will depend on the individual and on HTC policy.

Bleeding in the knee joint Cutaneous Adverse Effects
Also known as toxidermia, are skin manifestations resulting from systemic drug administration. These reactions range from mild erythematous skin lesions to much more severe reactions such as Lyell’s syndrome.

Pediatric toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome) Skin Reactions
An allergic reaction can cause rash, itching, burning, redness, bumps, hives, and swelling.

Urticaria (hives) allergic skin reaction Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome
A rare disorder of unknown origin that affects many body systems, including as the eyes, ears, skin, and the covering of the brain and spinal cord (the meninges). The most noticeable symptom is a rapid loss of vision.

Rapid loss in vision from Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome Capillary Leak Syndrome
Includes Term: Systemic Capillary Extravasation Syndrome. A rare disorder by acute and severe recurrent attacks associated with a rapid fall in blood pressure as a result of fluid leaks from smaller vessels called capillaries. Attacks often last several days and require emergency care. They are sometimes life threatening. SCLS occurs most often in adults and the disease is very rare in children.

Capillary leak syndrome results in dramatic swelling Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
An autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. It can affect the joints, skin, brain, lungs, kidneys, and blood vessels. Treatment can help, but this condition can’t be cured.

Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Petechiae
Includes: Petechial rash. Tiny purple, red, or brown spots on the skin. They usually appear on your arms, legs, stomach, and buttocks. You might also find them inside your mouth or on your eyelids. These pinpoint spots can be a sign of many different conditions — some minor, others serious. They can also appear as a reaction to certain medications. Though petechiae look like a rash, they’re actually caused by bleeding under the skin.

Petechiae (back of mouth) Purpura Annularis Telangiectodes
An uncommon pigmented purpuric eruption, which is characterized by symmetrical, purpuric, telangiectatic, and atrophic patches with a predilection for the lower extremities and buttocks.

Purpura Annularis Telangiectodes Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in your lungs. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from deep veins in the legs or, rarely, from veins in other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis). Because the clots block blood flow to the lungs, pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening.

Pulmonary Embolism Psoriasis
A chronic autoimmune condition that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells. This buildup of cells causes scaling on the skin’s surface. Inflammation and redness around the scales is fairly common. Typical psoriatic scales are whitish-silver and develop in thick, red patches. Sometimes, these patches will crack and bleed.

Psoriasis (scalp) Nephrotic Syndrome
Kidney disorder that causes your body to pass too much protein in your urine. Nephrotic syndrome is usually caused by damage to the clusters of small blood vessels in your kidneys that filter waste and excess water from your blood.

Nephrotic syndrome unine (left and middle) Healthy urine (right) Bullous Drug Eruption
Refers to adverse drug reactions that result in fluid-filled blisters or bullae. Blistering may be localised and mild, or widespread and severe, even life-threatening.

Bullous Drug Eruption (chin) Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
An aggressive and life-threatening syndrome of excessive immune activation. It most frequently affects infants from birth to 18 months of age, but the disease is also observed in children and adults of all ages.

Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (infant) Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in your lungs. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from deep veins in the legs or, rarely, from veins in other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis). Because the clots block blood flow to the lungs, pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening.

Pulmonary Embolism Blood Clots
A gelatinous mass of fibrin and blood cells formed by the coagulation of blood.

Blood Clot Thrombophilia
A blood disorder that makes the blood in your veins and arteries more likely to clot. This is also known as a “hypercoagulable” condition because your blood coagulates or clots more easily.

Thrombophilia iTTP episode
A rare, life-threatening thrombotic microangiopathy caused by severe ADAMTS13 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 13) deficiency, recurring in 30–50% of patients.

TTP results in absense of ADAMTS13 Refractory Status Epilepticus
Can be defined as status epilepticus (seizures) that continues despite treatment with benzodiazepines and one antiepileptic drug. RSE should be treated promptly to prevent morbidity and mortality; however, scarce evidence is available to support the choice of specific treatments.

Progression of Refractory Status Epilepticus Central Serous Retinopathy
A medical condition where fluid builds up behind the retina in the eye. It can cause sudden or gradual vision loss as the central retina detaches. This central area is called the macula.

Central Serous Retinopathy Cutaneous Reactions
A group of potentially lethal adverse drug reactions that involve the skin and mucous membranes of various body openings such as the eyes, ears, and inside the nose, mouth, and lips.

Cutaneous Reaction (inside of nose) Prion Disease
Prion diseases comprise several conditions. A prion is a type of protein that can trigger normal proteins in the brain to fold abnormally. Prion diseases or transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are a family of rare progressive neurodegenerative disorders that affect both humans and animals. They are distinguished by long incubation periods, characteristic spongiform changes associated with neuronal loss, and a failure to induce inflammatory response.

Creutzfelft-Jakob disease Pregnant Woman
Process-Related Impurities
CNS Inflammation
A disease that causes inflammation of the small arteries and veins in the brain and/or spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord make up the CNS. Intense interest in inflammation in the CNS has arisen from its potential role in diseases including acute brain injury, stroke, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, motor neurone disease, movement disorders and Alzheimer’s disease, and more recently some psychiatric disorders.

Craniocervical venous structure CNS Demyelination
A demyelinating disease is any condition that results in damage to the protective covering (myelin sheath) that surrounds nerve fibers in your brain, optic nerves and spinal cord. When the myelin sheath is damaged, nerve impulses slow or even stop, causing neurological problems.

The myelin sheath shields nerve fibers, like the sheath of electrical cables shields copper wire Orofacial
An orofacial myofunctional disorder (OMD) is when there is an abnormal lip, jaw, or tongue position during rest, swallowing or speech.

Illustration of orofacial myofunctional disorder Brain Haemorrhage
Includes Term: Lobar Hemorrhage. An emergency condition in which a ruptured blood vessel causes bleeding inside the brain.

Brain Haemorrhage Varicella Zoster Virus
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is so named because it causes two distinct illnesses: varicella (chickenpox), following primary infection, and herpes zoster (shingles), following reactivation of latent virus. Varicella is a highly contagious infection with an incubation period of 10–21 days, most commonly 14–16 days, after which a characteristic rash appears. Acute varicella may be complicated by secondary bacterial skin infections, haemorrhagic complications, cerebellitis, encephalitis, and viral and bacterial pneumonia.

herpes zoster (shingles) Nerve And Muscle Adverse Events
Many different possible neurologic adverse events including encephalitis, myelopathy, aseptic meningitis, meningoradiculitis, Guillain-Barré-like syndrome, peripheral neuropathy (including mononeuropathy, mononeuritis multiplex, and polyneuropathy) as well as myasthenic syndrome.

Aseptic meningitis Oculomotor Paralysis
Defines the decreased strength of a muscle, which produces a reduced rotational movement of the eyeball in the direction corresponding to the paralysed muscle. Partial deficit is called paresis, while full deficit is called paralysis.

Isolated oculomotor nerve palsy Parsonage-Turner Syndrome
An neurological disorder characterized by rapid onset of severe pain in the shoulder and arm. This acute phase may last for a few hours to a few weeks and is followed by wasting and weakness of the muscles (amyotrophy) in the affected areas.

Acute Macular Neuroretinopathy
A rare, acquired retinal disorder characterised by transient or permanent visual impairment accompanied by the presence of reddish-brown, wedge-shaped lesions in the macula, the apices of which tend to point towards the fovea.

Multicolor imaging in the diagnosis and follow up of type 2 acute macular neuroretinopathy Lipschütz ulcers (Vaginal ulcers)
Acute genital ulceration, also known as “Lipschütz ulcer” or “ulcus vulvae acutum,” is an uncommon, self-limited, nonsexually transmitted condition characterized by the rapid onset of painful, necrotic ulcerations of the vulva or lower vagina.

Acute genital ulcer (Lipschutz ulcer) Amyotrophic Neuralgia
A disorder characterized by episodes of severe pain and muscle wasting (amyotrophy) in one or both shoulders and arms. Neuralgic pain is felt along the path of one or more nerves and often has no obvious physical cause.

Amyotrophic Neuralgia Polyarthralgia
Pain in multiple joints. Symptoms may include pain, tenderness, or tingling in the joints and reduced range of motion. Polyarthralgia is similar to polyarthritis, but it doesn’t cause inflammation. Lifestyle changes, home remedies, and medication can help manage the symptoms.

Polyarthralgia Thyroiditis
The swelling, or inflammation, of the thyroid gland and can lead to over- or under-production of thyroid hormone. A thyroid storm — or thyroid crisis — can be a life-threatening condition. It often includes a rapid heartbeat, fever, and even fainting. Symptoms may include pain in the throat, feeling generally unwell, swelling of the thyroid gland and, sometimes, symptoms of an overactive thyroid gland or symptoms of an underactive thyroid gland.

Inflammation of the thyroid Keratolysis (Corneal Melting)
A common prelude to the development of corneal perforation. This process occurs from conditions such as infections, sterile inflammation, or surgical/chemical injury to the cornea. Collectively, these conditions are a significant cause for blindness world-wide.

Keratolysis (Corneal Melting) Arthritis
The swelling and tenderness of one or more joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.

Thymic hyperplasia
A condition in which the thymus gland is inflamed. It is often accompanied by autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis and rheumatoid arthritis.

Human thymus Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome
A rare disorder characterized by severe periorbital headaches, along with decreased and painful eye movements (ophthalmoplegia). Symptoms usually affect only one eye (unilateral). In most cases, affected individuals experience intense sharp pain and decreased eye movements.

Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome Hailey-Hailey Disease
Also known as benign chronic pemphigus, is a rare skin condition that usually appears in early adulthood. The disorder is characterized by red, raw, and blistered areas of skin that occur most often in skin folds, such as the groin, armpits, neck, and under the breasts.

Hailey-Hailey Disease (under breast) Acute Lympholysis
Interstitial Lung Disease
Describes a large group of disorders, most of which cause progressive scarring of lung tissue. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream.

Interstitial Lung Disease Vesiculobullous Cutaneous Reactions
A vesiculobullous lesion of the skin encompasses a group of dermatological disorders with protean clinicopathological features. They usually occur as a part of the spectrum of various infectious, inflammatory, drug-induced, genetic, and autoimmune disorders.

Bullous Pemphigoid Associated With COVID-19 Vaccines Hematologic Conditions
Hemolysis
Headache

Headache varieties Acute Coronary Syndrome
Any condition brought on by a sudden reduction or blockage of blood flow to the heart.

Acute Coronary Syndrome ANCA Glomerulonephritis
The term we use when ANCA vasculitis has affected or involved the kidneys, and when this happens there is inflammation and swelling in the kidney filters, meaning that the body’s own immune system injures its cells and tissues.

ANCA Glomerulonephritis (inflammation and swelling of the kidney filters) Neurologic Phantosmia
An olfactory hallucination perceived when no odorants are present. Both the olfactory distortions are typically described as unpleasant.

Neurologic Phantosmia – detecting smells that are not there Uveitis
Includes terms: bilateral. A form of eye inflammation. It affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea). Uveitis warning signs often come on suddenly and get worse quickly. They include eye redness, pain and blurred vision.

Uveitis of right eye Pathophysiologic Alterations
Deranged function in an individual or an organ due to a disease. For example, a pathophysiologic alteration is a change in function as distinguished from a structural defect.

Nephropathy of kidney Inflammatory Myositis
Inflammatory myopathies are a group of diseases that involve chronic (long-standing) muscle inflammation, muscle weakness, and, in some cases, muscle pain. Myopathy is a general medical term used to describe a number of conditions affecting the muscles. All myopathies cause muscle weakness.

Inflammatory Myositis Still’s Disease
A rare type of inflammatory arthritis that features fevers, rash and joint pain. Some people have just one episode of adult Still’s disease. In other people, the condition persists or recurs. This inflammation can destroy affected joints, particularly the wrists.

Still’s Disease Pityriasis Rosea
A skin rash that sometimes begins as a large spot on the chest, abdomen or back, followed by a pattern of smaller lesions.

Pityriasis Rosea Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
The acute-onset form of eosinophilic pneumonia, a lung disease caused by the buildup of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the lungs. It is characterized by a rapid onset of shortness of breath, cough, fatigue, night sweats, and weight loss.

Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia Sweet’s Syndrome
An uncommon skin condition marked by a distinctive eruption of tiny bumps that enlarge and are often tender to the touch. They can appear on the back, neck, arms or face. Sweet’s syndrome, also called acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is an uncommon skin condition.

Sweet’s Syndrome (back and neck) Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hearing loss caused by damage to the inner ear or the nerve from the ear to the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss is permanent.

Human ear canal Serious Adverse Events Among Health Care Professionals
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
A life-threatening skin disorder characterized by a blistering and peeling of the skin. This disorder can be caused by a drug reaction—often antibiotics or anticonvulsives.

Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Ocular Adverse Events
The majority of ocular immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are mild, low-grade, non-sight threatening, such as blurred vision, conjunctivitis, and ocular surface disease.

Blurred vision Depression
A common and serious medical illness that negatively affects how you feel, the way you think and how you act. Depression causes feelings of sadness and/or a loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed.
Total Papers: 1

Artistic illustration Pancreas Allograft Rejection
When the body’s blood cells identify the pancreas as foreign and begin mounting an army of cells to attack the transplanted organ. Although acute rejection can happen at any time, about 15 to 25% of pancreas acute rejection occurs within the first three months after transplant.

Pancreas Acute Hemichorea-Hemibalismus
Hemiballismus is characterized by high amplitude, violent, flinging and flailing movements confined to one side of body and hemichorea is characterized by involuntary random-appearing irregular movements that are rapid and non-patterned confined to one side of body.
Alopecia Areata
Sudden hair loss that starts with one or more circular bald patches that may overlap. Alopecia areata occurs when the immune system attacks hair follicles and may be brought on by severe stress.

Alopecia Areata Graves’ Disease
An autoimmune disorder that causes hyperthyroidism, or overactive thyroid. With this disease, your immune system attacks the thyroid and causes it to make more thyroid hormone than your body needs. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of your neck. Thyroid hormones control how your body uses energy, so they affect nearly every organ in your body—even the way your heart beats. If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can cause serious problems with the heart, bones, muscles, menstrual cycle, and fertility. During pregnancy, untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to health problems for the mother and baby. Graves’ disease also can affect your eyes and skin.

Images of extrathyroidal features of Graves’ disease Cardiovascular Events
Metabolic Syndrome
A cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke and diabetes.
Eosinophilic Dermatosis
Eosinophilic skin diseases, commonly termed as eosinophilic dermatoses, refer to a broad spectrum of skin diseases characterized by eosinophil infiltration and/or degranulation in skin lesions, with or without blood eosinophilia. The majority of eosinophilic dermatoses lie in the allergy-related group, including allergic drug eruption, urticaria, allergic contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and eczema.

Eosinophilic Dermatosis Hypercoagulability
The tendency to have thrombosis as a result of certain inherited and/or acquired molecular defects. Clinical manifestations of hypercoagulability can be devastating and even lethal.
Neuroimaging Findings in Post COVID-19 Vaccination

Spectrum of Neuroimaging Findings in Post-COVID-19 Vaccination Urticaria
A rash of round, red welts on the skin that itch intensely, sometimes with dangerous swelling, caused by an allergic reaction.

Urticaria Central Vein Occlusion
A blockage of this vein that causes the vein to leak blood and excess fluid into the retina. This fluid often collects in the area of the retina responsible for central vision called the macula. When the macula is affected, central vision may become blurry. The second eye will develop vein occlusion in 6-17% of cases. There’s no cure for retinal vein occlusion. Your doctor can’t unblock the retinal veins. What they can do is treat any complications and protect your vision.

Central Vein Occlusion Thrombophlebitis
A condition in which a blood clot in a vein causes inflammation and pain.

Thrombophlebitis Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Chest Pain
Acute Inflammatory Neuropathies
Encompass groups of heterogeneous disorders characterized by pathogenic immune-mediated hematogenous leukocyte infiltration of peripheral nerves, nerve roots or both, with resultant demyelination or axonal degeneration or both, and the pathogenesis of these disorders remains elusive.
Brain Death
Irreversible cessation of all functions of the entire brain, including the brain stem. A person who is brain dead is dead.
Kounis Syndrome
The concurrence of acute coronary syndromes with conditions associated with mast cell activation, such as allergies or hypersensitivity and anaphylactic or anaphylactoid insults that can involve other interrelated and interacting inflammatory cells behaving as a ‘ball of thread’.
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
A type of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. It is a high grade (aggressive) lymphoma that affects blood cells called T cells. High grade lymphomas tend to grow more quickly than low grade lymphomas. AITL usually affects older people, typically around the age of 70, is typically aggressive with a median survival of fewer than 3 years, even with intensive treatment.
Gastroparesis
A condition that affects the stomach muscles and prevents proper stomach emptying.
Asthma
A condition in which a person’s airways become inflamed, narrow and swell and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe. Asthma can be minor or it can interfere with daily activities. In some cases, it may lead to a life-threatening attack.
Safety Monitoring of the Janssen Vaccine
Myocardial Injury
Refers to the cell death of cardiomyocytes and is defined by an elevation of cardiac troponin values. It is not only considered a prerequisite for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction but also an entity in itself and can arise from non-ischaemic or non-cardiac conditions.
Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases
Rheumatic diseases are autoimmune and inflammatory diseases that cause your immune system to attack your joints, muscles, bones and organs. Rheumatic diseases are often grouped under the term “arthritis” — which is used to describe over 100 diseases and conditions.
Neurological Autoimmune Diseases
If you have a neurological autoimmune disease, your immune system may be overly active and mistakenly attack healthy cells. These include central nervous system demyelinating disorders such as multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica, paraneoplastic, and other autoimmune encephalomyelitis and autoimmune inflammatory myositis and demyelinating neuropathies.
V-REPP
Vaccine-related eruption of papules and plaques.
Herpes Simplex Virus
A virus causing contagious sores, most often around the mouth or on the genitals.
Related Material
- A Library of Dr Trozzi material regarding covid “vaccines”
- Covid “Vaccines”; How Dangerous are They? Dr Mark Trozzi. June 4, 2021. A thorough investigation of the science behind the Covid “vaccines” used in the Western World.
- More Resources from The Covid Vaccine Injuries Community
source:1000 peer reviewed articles on “Vaccine” injuries (drtrozzi.org)
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.